Preface to the Application
Dairy products are an important nutritional source in the human diet, especially for infants and children. Detecting the concentrations of major elements such as Na, K, Mg, Ca, P and trace elements such as Fe, Mn, Cu, Zn can provide valuable nutritional information. Additionally, it is necessary to detect trace harmful elements such as As, Cr, Hg, and Pb in dairy products to monitor potential contamination from environmental or processing/transportation processes. Compared with graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrometry, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) features high sensitivity, wide elemental coverage, broad linear range, and minimal interference, making it highly suitable for simultaneous multi-element analysis. While analyzing trace elements, its analytical range can be expanded to include major elements, significantly improving detection efficiency and sample throughput. It is an ideal choice for multi-element analysis in food samples. This paper refers to the national food safety standard GB 5009.268-2016, using a fully automated microwave digestion robot to rapidly and fully automatically digest infant formula milk powder and milk samples. By applying the ICP-MS method with a single injection and using the intelligent electronic dilution function, it simultaneously analyzes 9 nutritional elements and 4 harmful elements. This achieves high-throughput and accurate quantification of both high- and low-content elements in a single injection without any switching.
Conclusion of the Article
The P3 Ultra-Power Microwave Robot can fully automatically perform microwave digestion on dairy product samples, while the iQuad 2300 ICP-MS enables accurate quantitative analysis of 13 elements in the digested dairy products. By using the instrument’s kinetic energy discrimination mode and automatic tuning function, method development can be simplified. With the unique electron dilution function and the high sensitivity of the iQuad 2300 system, it is possible to simultaneously analyze major elements (such as Na, K, Ca, Mg) and trace elements (including Cr, As, Pb, Hg) in a single injection. The accuracy of the method was evaluated by analyzing 9 nutritional elements in quality control samples and conducting spike recovery tests on 4 contaminant elements near the method detection limit concentration. Good matching with standard values or excellent recovery rates were obtained in all cases. The iQuad 2300 ICP-MS method is suitable for routine multi-element analysis of trace elements and high-concentration elements in foods, ensuring quality control of nutritional elements and contaminants.
Highlights of the Solution
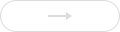
The measurement was performed using the iQuad 2300 kinetic energy discrimination mode (He collision mode), which effectively reduces common matrix polyatomic ion interferences. Infant formula milk powder usually contains high levels of nutritional elements such as K and Na, while heavy metals are present at trace or ultra-trace levels. By utilizing the unique electron dilution function of the iQuad 2300, different dilution factors were set for the elements to be measured, allowing simultaneous analysis results of both nutritional elements and heavy metals in a single ICP-MS injection. To verify the reliability of the analysis for four elements (As, Hg, Pb, and Cr), spiked recovery tests were conducted for these elements. Samples were spiked at low, medium, and high concentrations, and the spiked recovery rates for each element were calculated, as listed in Table 5. The recovery rates of all elements at various concentrations fell within the range of 90%–110%, indicating that the analysis results for heavy metal elements are reliable.