Application Preface
As an important plant used both as food and medicine, ginger is widely applied in food seasoning, traditional medicine, and modern functional products worldwide. Its unique bioactive components (such as gingerols and volatile oils) have been confirmed to possess pharmacological effects including anti-inflammation, anti-oxidation, and anti-bacterial properties. In recent years, studies have shown that the contents of trace elements (e.g., zinc, selenium) and heavy metal elements (e.g., thallium, antimony, arsenic) in ginger not only affect its medicinal value and food safety but may also have direct or indirect impacts on human health through food chain transmission. Therefore, systematic analysis of the multi-element composition in ginger is of great significance for evaluating its nutritional efficacy, quality control, and potential risks. At present, traditional methods for elemental analysis in plant matrices (such as atomic absorption spectrometry and spectrophotometry) are often limited by issues such as low single-element detection efficiency, insufficient sensitivity, or severe matrix interferences. Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry (ICP-MS) has become an ideal tool for trace element analysis in complex biological samples due to its high sensitivity, wide dynamic linear range, and capability for simultaneous multi-element detection. Aiming at the special food matrix of ginger, this paper adopts microwave digestion combined with ICP-MS technology. By optimizing pretreatment conditions and mass spectrometry parameters, it aims to establish an efficient and accurate multi-element detection method for ginger, providing a scientific basis for quality evaluation, safety supervision, and medicinal value development of ginger resources. In this paper, the Hansel iQuad 2300 and P3 microwave digestion robot were used for quantitative analysis of 17 elements in the ginger powder quality control sample GBW10202.
Article Conclusion
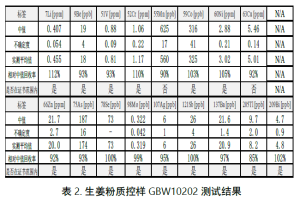
1. In the analysis of the ginger powder quality control sample GBW10202, the external standard method widely used in the industry was employed for testing, and matrix effects were eliminated through internal standard and instrument parameter optimization. Finally, rapid determination of 17 elements was achieved, with 15 elements meeting the certified values and the errors of the other 2 elements within 10% of the certified median values.
2. This test demonstrates that the iQuad 2300 has strong matrix tolerance and quantification capabilities, enabling accurate and rapid quantification of multiple elements in ginger powder quality control samples.
Highlights of the Scheme
In this experiment, only one flow rate was required for the helium KED mode. The iQuad 2300’s unique electronic dilution design enables it to differentially eliminate polyatomic ion mass spectrometry interferences and intelligently adjust sensitivity at the same flow rate. Seventeen elements were evaluated in this experiment. Fifteen elements fell within the certified value range, and the test results of the other two elements were within a 10% error range of the certified median values. The test results for the ginger powder samples and the corresponding element mass numbers are summarized in the following table: