Application Preface
As global pharmaceutical regulations converge, the International Council for Harmonisation (ICH) Q3D, ICH Q2, and United States Pharmacopeia (USP) general chapters have jointly advanced risk assessment and control requirements for elemental impurities in pharmaceuticals. Traditional heavy metal detection methods, limited by low sensitivity and poor selectivity, can no longer meet the precise quantification needs for trace elemental impurities. Against this backdrop, inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS) has emerged as the core technology for elemental impurity analysis under the ICH Q3D framework, leveraging its ultra-low detection limits (ppt level), multi-element simultaneous analysis capabilities, and isotope resolution.
ICH Q3D (R2) classifies 24 elements into Category 1 (e.g., As, Cd, Hg, Pb), Category 2A/2B (e.g., Co, Ni), and Category 3 (e.g., Cu, Li) based on elemental toxicity and administration routes (oral, injection, inhalation, transdermal), and sets Permitted Daily Exposure (PDE) limits. ICP-MS can meet the detection requirements for all categories of elements, ensuring accuracy in complex samples (such as high-salt injectables). However, ICP-MS analysis still faces technical challenges: signal suppression caused by matrix effects. While manually increasing the dilution factor can mitigate matrix effects, it may introduce contamination that affects the stability and accuracy of results. Additionally, mass spectral interferences caused by certain substances introduced in pharmaceuticals or during sample pretreatment—such as ClO interference on V—pose further challenges. With the deep coordination between the Chinese Pharmacopoeia and ICH, and the expansion of hyphenated technologies (such as HPLC-ICP-MS), this technology will play a more critical role in the full lifecycle monitoring of pharmaceuticals. This paper uses the Hengsheng iQuad2300 ICP-MS to conduct methodological validation on normal saline according to ICH and USP requirements, following industry practices in the pharmaceutical sector.
Conclusions of the Article
1. This method validation demonstrates the capability of the Hengsheng iQuad 2300 ICP-MS to address elemental impurity analysis in accordance with ICH and USP specifications. Even for high-salt matrices, it is fully competent to analyze 24 elements at a concentration of 10% J.
2. Due to the flexibility of the △H parameter in the analytical method, the time for helium gas switching can be reduced, improving analytical efficiency and method flexibility. This enables the iQuad 2300 to analyze 24 elements using only one helium flow rate.
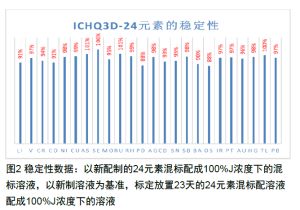
3. This experiment confirms the solution stability of 24 elements, providing a reference for others. Commercially available normal saline generally has good control over elemental impurities.
Highlights of the Plan
**Solution Stability Issues** When intentionally added, the ICH guidelines may require testing for 24 elements. These elements have different chemical properties, and when individual standards are combined into a mixed standard, solution stability can significantly affect results. This is particularly true for stock mixed standards, which are cumbersome to prepare. Studying their stability is valuable for reducing workload, improving analytical accuracy, and minimizing anomalies. Data show that the stability of the 24 investigated elements ranges from 88% to 106%, meeting basic analytical requirements.